Portal:Libertarianism
Introduction
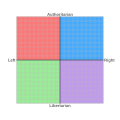
Libertarianism (from French: libertaire, itself from the Latin: libertas, lit. 'freedom') is a political philosophy that upholds liberty as a core value. Libertarians seek to maximize autonomy and political freedom, emphasizing equality before the law and civil rights to freedom of association, freedom of speech, freedom of thought and freedom of choice. Libertarians are often skeptical of or opposed to authority, state power, warfare, militarism and nationalism, but some libertarians diverge on the scope of their opposition to existing economic and political systems. Various schools of libertarian thought offer a range of views regarding the legitimate functions of state and private power. Different categorizations have been used to distinguish various forms of Libertarianism. Scholars distinguish libertarian views on the nature of property and capital, usually along left–right or socialist–capitalist lines. Libertarians of various schools were influenced by liberal ideas.
In the mid-19th century, libertarianism originated as a form of left-wing politics such as anti-authoritarian and anti-state socialists like anarchists, especially social anarchists, but more generally libertarian communists/Marxists and libertarian socialists. These libertarians sought to abolish capitalism and private ownership of the means of production, or else to restrict their purview or effects to usufruct property norms, in favor of common or cooperative ownership and management, viewing private property in the means of production as a barrier to freedom and liberty. While all libertarians support some level of individual rights, left-libertarians differ by supporting an egalitarian redistribution of natural resources. Left-libertarian ideologies include anarchist schools of thought, alongside many other anti-paternalist and New Left schools of thought centered around economic egalitarianism as well as geolibertarianism, green politics, market-oriented left-libertarianism and the Steiner–Vallentyne school. After the fall of the Soviet Union, libertarian socialism grew in popularity and influence as part of anti-war, anti-capitalist and anti- and alter-globalisation movements. (Full article...)
Selected article
Libertarian socialism (or socialist libertarianism) is a group of anti-authoritarian political philosophies inside the socialist movement that rejects socialism as centralized state ownership and control of the economy.
Libertarian socialism also rejects the state itself, is close to and overlaps with left-libertarianism and criticizes wage labour relationships within the workplace, instead emphasizing workers' self-management of the workplace and decentralized structures of political organization. It asserts that a society based on freedom and justice can be achieved through abolishing authoritarian institutions that control certain means of production and subordinate the majority to an owning class or political and economic elite. Libertarian socialists advocate for decentralized structures based on direct democracy and federal or confederal associations such as libertarian municipalism, citizens' assemblies, trade unions and workers' councils.
All of this is generally done within a general call for libertarian and voluntary human relationships through the identification, criticism and practical dismantling of illegitimate authority in all aspects of human life. As such, libertarian socialism within the larger socialist movement seeks to distinguish itself both from Leninism/Bolshevism and from social democracy.
Past and present political philosophies and movements commonly described as libertarian socialist include anarchism as well as autonomism, communalism, participism, guild socialism, revolutionary syndicalism and libertarian Marxist philosophies such as council communism and Luxemburgism as well as some versions of utopian socialism and individualist anarchism.
Selected quote
| “ | I remember the occasion when a fellow graduate student at Columbia from Sweden wanted to take me downtown to a restaurant for a Swedish meal and introduced me to the Swedish drink aquavit. This was a restaurant at which this Swedish fellow had been getting aquavit all during Prohibition; they had been selling it to him. And this was just after the repeal of Prohibition. We went there and he asked them for some aquavit. They said, "Oh, no, we haven't gotten our license yet." And finally, he talked to them in Swedish and persuaded them to take us into the back where they gave us a glass of aquavit apiece. Now that shows the absurdity of it.
Prohibition was repealed in 1933 when I was 21 years old, so was a teenager during most of Prohibition. Alcohol was readily available. Bootlegging was common. Any idea that alcohol prohibition was keeping people from drinking was absurd. There were speakeasies all over the place. But more than that. We had this spectacle of Al Capone, of the hijackings, of the gang wars... Anybody with two eyes could see that this was a bad deal, that you were doing more harm than good. In addition, I became an economist. And as an economist, I came to recognize the importance of markets and of free choice and of consumer sovereignty and came to discover the harm that was done when you interfered with them. The laws against drugs were passed in 1914, but there was no very great enforcement of it. |
” |
| — Milton Friedman (1912–2006) America's Drug Forum (1991) |
Selected picture
 |
General images
Selected biography -

Milton Friedman (/ˈfriːdmən/ ; July 31, 1912 – November 16, 2006) was an American economist and statistician who received the 1976 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for his research on consumption analysis, monetary history and theory and the complexity of stabilization policy. With George Stigler, Friedman was among the intellectual leaders of the Chicago school of economics, a neoclassical school of economic thought associated with the work of the faculty at the University of Chicago that rejected Keynesianism in favor of monetarism until the mid-1970s, when it turned to new classical macroeconomics heavily based on the concept of rational expectations. Several students, young professors and academics who were recruited or mentored by Friedman at Chicago went on to become leading economists, including Gary Becker, Robert Fogel, and Robert Lucas Jr.
Friedman's challenges to what he called "naive Keynesian theory" began with his interpretation of consumption, which tracks how consumers spend. He introduced a theory which would later become part of mainstream economics and among the first to propagate the theory of consumption smoothing. During the 1960s, he became the main advocate opposing Keynesian government policies, and described his approach (along with mainstream economics) as using "Keynesian language and apparatus" yet rejecting its initial conclusions. He theorized that there existed a natural rate of unemployment and argued that unemployment below this rate would cause inflation to accelerate. He argued that the Phillips curve was in the long run vertical at the "natural rate" and predicted what would come to be known as stagflation. Friedman promoted a macroeconomic viewpoint known as monetarism and argued that a steady, small expansion of the money supply was the preferred policy, as compared to rapid, and unexpected changes. His ideas concerning monetary policy, taxation, privatization, and deregulation influenced government policies, especially during the 1980s. His monetary theory influenced the Federal Reserve's monetary policy in response to the global financial crisis of 2007–2008. (Full article...)Related portals
Parent portals
Socio-political portals
Topics
Categories
Points of interest
| Points of interest related to Libertarianism on Wikipedia: History – Portal – Category – WikiProject – Alerts – Deletions – Assessment |
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus